Healthcare Costs and Private Insurance in 2025: What You Need to Know
When you think about healthcare costs, the total money spent on medical services, including insurance, drugs, and procedures. Also known as medical expenses, it’s not just about what you pay at the doctor’s office—it’s about how the system is built to favor those who can afford it. In 2025, the gap between what people pay and what they get grew wider. In the US, buying private health insurance alone can cost between $300 and $900 a month. Even with subsidies, many still face high deductibles and surprise bills. Meanwhile, in the UK, the NHS offers free care at the point of use—but access delays and private options create a two-tier system where money often decides speed and comfort.
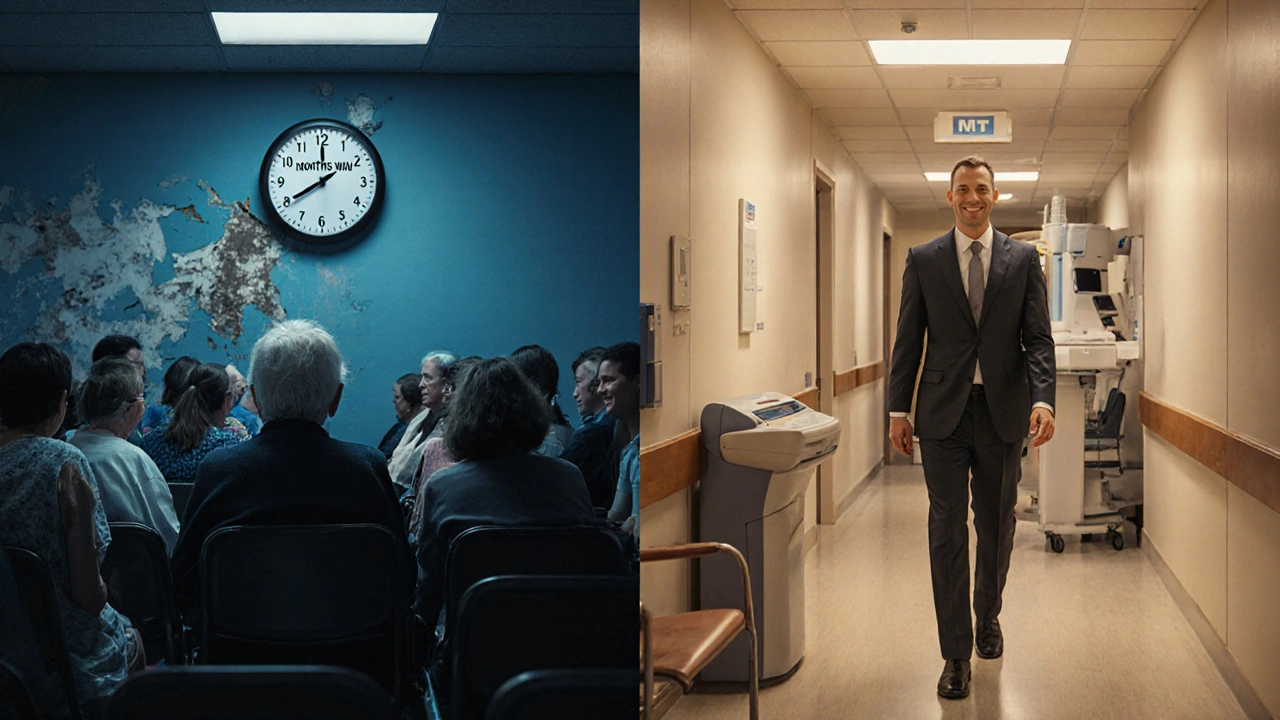
private insurance, a health coverage plan purchased directly by individuals or employers, not funded by the government. Also known as individual health insurance, it promises faster access but rarely delivers fairness. The data shows it’s not about choice—it’s about who can jump the queue. Those with private coverage get quicker scans, shorter waits, and priority surgery. Those without? They wait. Sometimes for months. Sometimes for years. And sometimes, the wait costs them more than money—it costs them time, mobility, even life. This isn’t a flaw in the system. It’s how the system works.
And it’s not just about access. UK healthcare, the publicly funded system providing free medical services to residents, largely through taxation. Also known as NHS, it’s often praised for its fairness—but its strain is visible in long waits for non-emergency care. Meanwhile, US medical expenses, the high out-of-pocket and insurance-driven costs that make healthcare the leading cause of bankruptcy in America. Also known as medical bills, they’re not just high—they’re unpredictable. A single hospital stay can wipe out savings. A missed paycheck can mean skipping meds. The US spends nearly 2.5 times more per person than the UK, yet outcomes aren’t better. In fact, life expectancy is lower.
What’s clear from the posts this month is that healthcare isn’t just about medicine. It’s about money, power, and who gets left behind. From the biggest side effect of gabapentin to the riskiest cosmetic surgery, from top surgery funding to dental implant longevity—every topic ties back to one truth: if you’re not wealthy, the system makes it harder to stay healthy. And if you’re trying to navigate this alone, you’re not just lost—you’re at risk.
Below, you’ll find real, no-fluff guides on what these costs actually look like, how to protect yourself, what alternatives exist, and who’s being left out. No marketing. No hype. Just facts, risks, and options—because your health shouldn’t depend on your bank account.
How Much Does It Cost to Buy Health Insurance on Your Own in the US?
Buying health insurance on your own in the US can cost between $300 and $900 a month, depending on your age, income, and location. Subsidies can cut costs significantly - here’s how to find the right plan without overpaying.
Why is private healthcare unfair?
Private healthcare isn't about choice-it's about who can afford to jump the line. Those with money get faster care. Those without wait, sometimes with deadly consequences. This is how inequality becomes medical policy.
What Is the 20-Minute Permanent Facelift? Real Results or Just a Myth?
The 20-minute permanent facelift is a marketing myth. Learn what thread lifts really do, how long results last, the real risks, and safer alternatives in the UK.
What Age Do You Lose Insurance Coverage? Private Health Rules Explained
Most private health insurance plans stop covering you at age 26. Learn when coverage ends, what options you have after, and how to avoid being left uninsured.
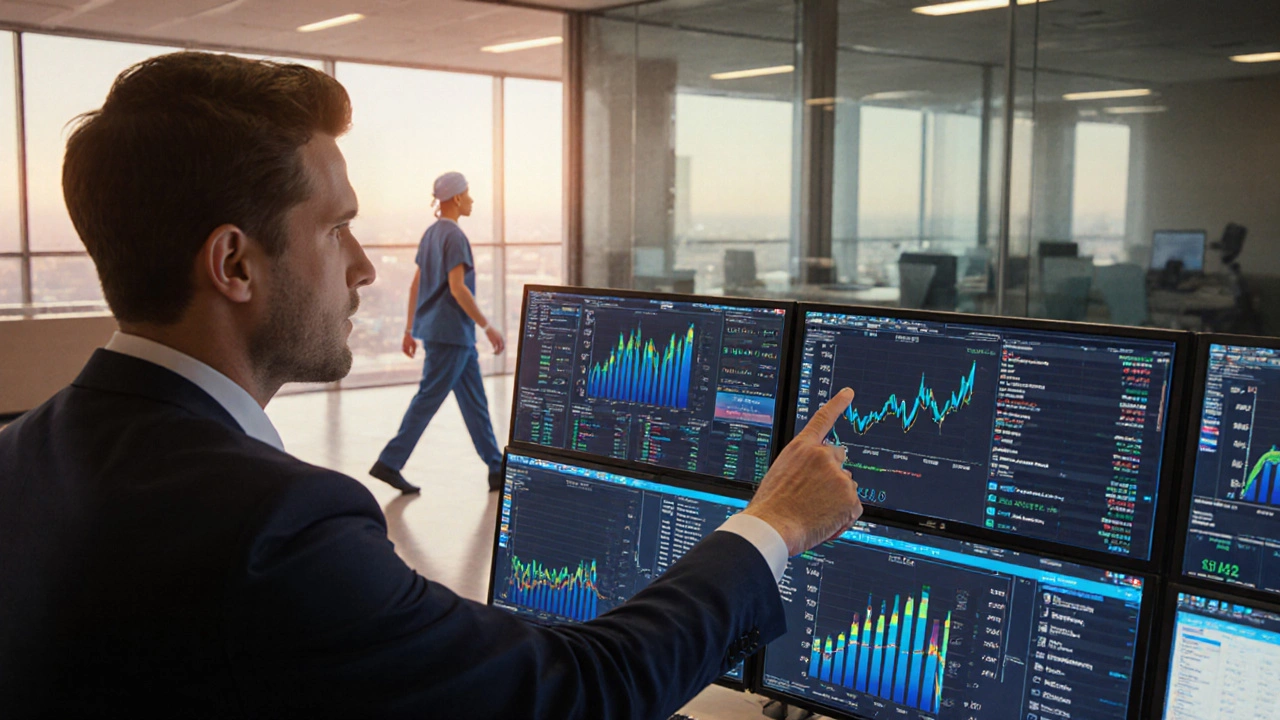
Most Profitable Medical Specialties for Hospital Revenue
Discover which medical specialties generate the most hospital revenue, why they’re profitable, and what patients should know when planning private surgery.
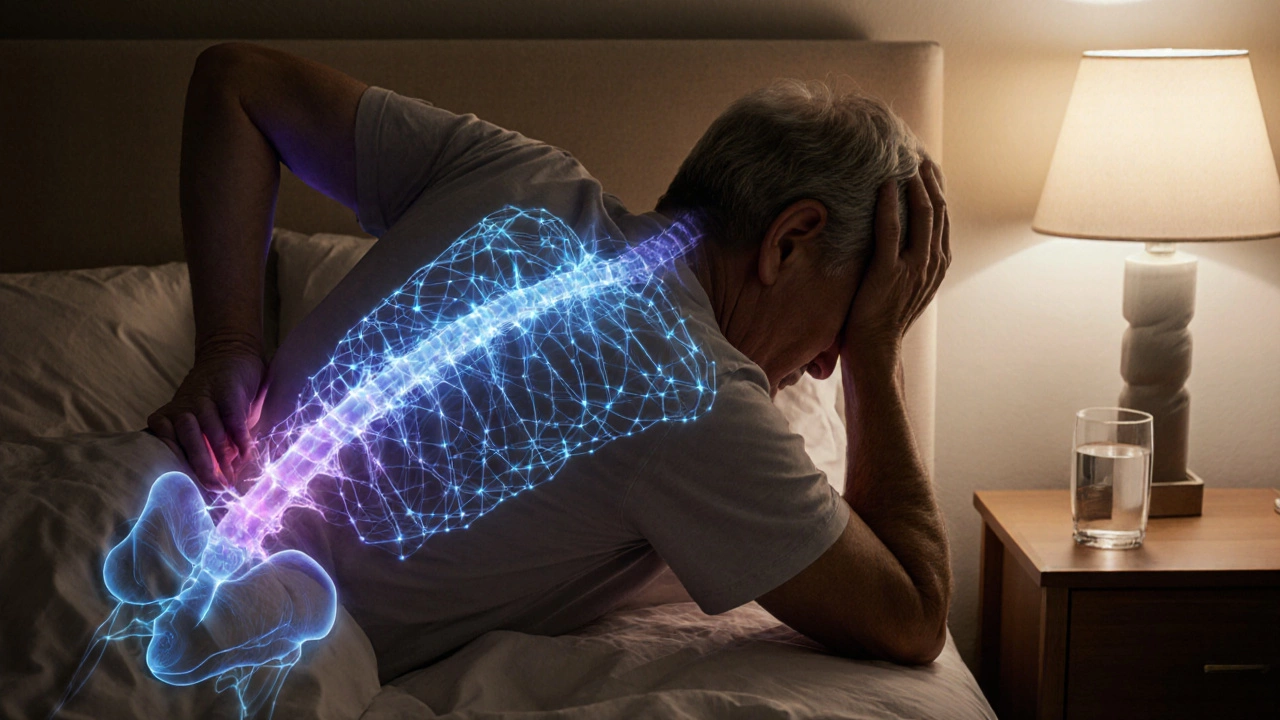
Can Chronic Pain Be Overcome? Effective Treatment Strategies Explained
Explore whether chronic pain can be overcome with a blend of education, movement, therapy, medication and interdisciplinary programs for lasting relief.
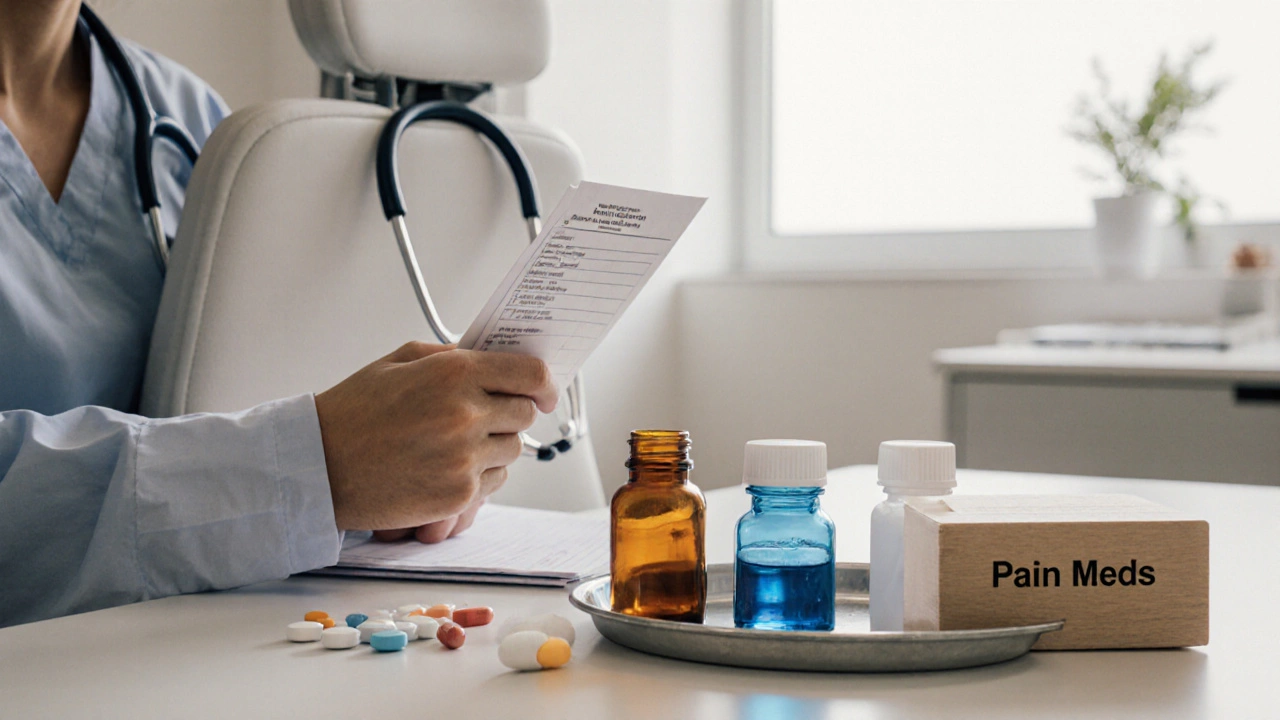
Common Pain Medications Doctors Prescribe: An Overview
Discover the most common pain medications doctors prescribe, when they choose each type, key side‑effects, and how non‑drug therapies fit into treatment.
What are the three types of physiotherapy? Explained
Learn the three core physiotherapy types-manual, exercise, and electrotherapy-how they differ, when to use each, and tips for finding a qualified physiotherapist near you.
Private vs Public Healthcare: Key Differences Explained
Explore the core differences between private and public healthcare, covering funding, costs, wait times, quality, and how to choose the right option for you.
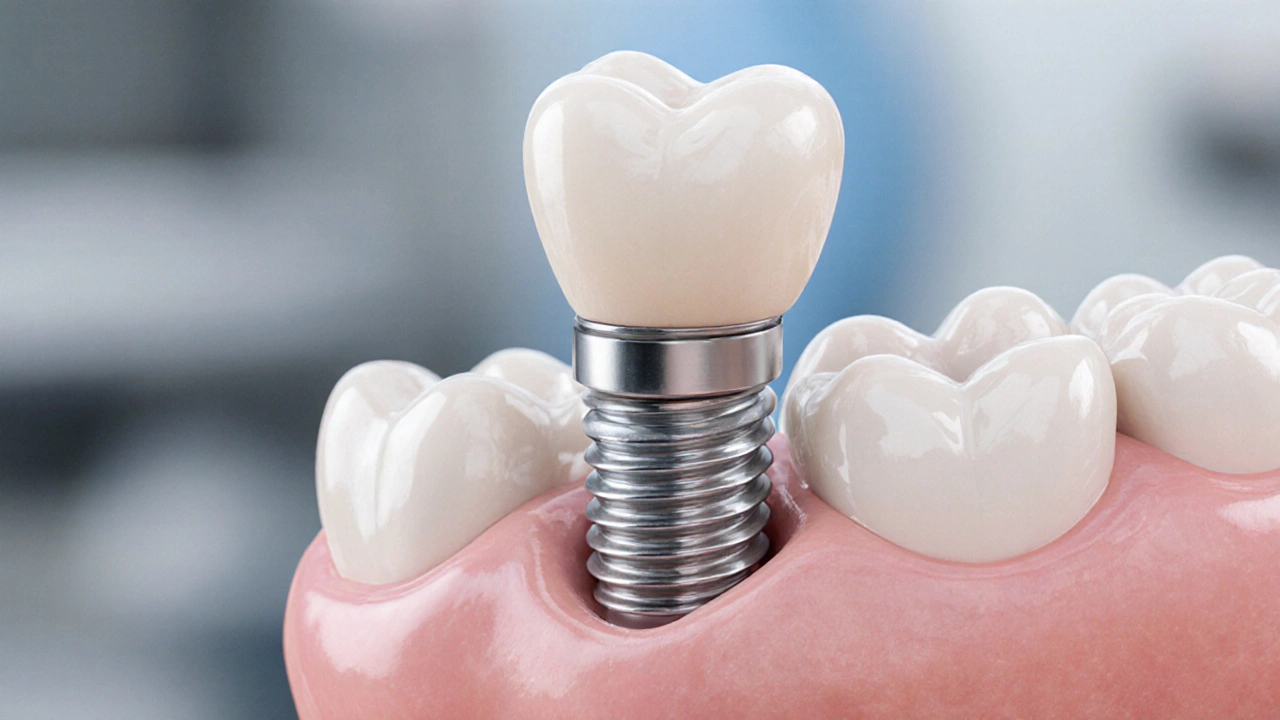
How Long Do Dental Implants Last? Lifespan, Care & Costs Explained
Discover how long dental implants truly last, the factors that affect their lifespan, and practical tips to keep them healthy for decades.
What Is the Biggest Side Effect of Gabapentin? - Risks Explained
Learn why dizziness and fall risk are the biggest side effect of gabapentin, who’s most vulnerable, and how to manage or avoid it.
How to Find a Good GP Near You - Step‑by‑Step Guide
Learn a practical, step‑by‑step way to locate a reliable GP near you, covering directories, accreditation, reviews, insurance and trial visits.