 Jul, 20 2025
Jul, 20 2025
Imagine being wheeled into an operating room, knowing your procedure could turn that place into what looks like a movie scene from a horror flick. The scariest part? For a handful of surgeries, that's not far from the truth. Surgeons talk about 'blood loss' all the time, but in some cases, it's not just a technical term—it's a life-or-death challenge where entire teams scramble to keep a patient from bleeding out on the table. Surgical blood loss is never just about numbers, but when things go wrong, those numbers get downright terrifying.
Why Do Some Surgeries Get So Bloody?
The human body has somewhere between 8 and 12 pints of blood, give or take. Lose more than 40% of that, and you've crossed into dangerous territory, where organs start to fail and things can spiral in minutes. So what makes some surgeries so much more blood-soaked than others? Three words: location, complexity, and speed. If a procedure involves cutting near or into major arteries or veins—or if an organ is packed with its own network of blood vessels—every slice matters. Add trauma, like car crashes or gunshot wounds, and you've got situations where the bleeding doesn't wait politely for the surgeon to get ready—it just erupts.
Some parts of your body are surprisingly vascular. The liver is one exaggerated example. It filters nearly 1.5 liters of blood every single minute. The pelvis is another danger zone, since it's surrounded by arteries feeding the legs. Head injuries and heart surgeries also take the cake because the brain and heart can't go for even a few seconds without steady blood flow.
To make things trickier, some patients come into the operating room already bleeding, maybe from a ruptured aneurysm or a horrible accident. There, surgeons have maybe minutes (sometimes less) to patch the leak, or the story ends right there. Nothing is predictable about managing this kind of bleeding—each blood vessel is a potential disaster, so the entire team has to stay on red alert, often running through dozens of units of blood in a matter of hours.
You might wonder, does technology help? Definitely. Surgeons now use cauterizing tools, cell savers to recycle spilled blood, and better clotting medications. Yet, when a vessel the width of your thumb bursts, there’s simply no gadget that can make the bleeding vanish in a snap. It’s skill, teamwork, and a bit of luck.
The Top Contenders for the Bloodiest Surgery
If you ask ten surgeons what the bloodiest surgery is, you’ll get different answers depending on their specialty and what week they've had. Still, a few procedures pop up on every surgeon’s short list. Bloodiest surgery is a hard title to crown, but let's run through the highest-risk candidates based on known research, survival rates, and horror stories often traded in the break room.
- Liver Transplant and Resection: Easily at the top. Surgeons often report blood losses upwards of 10 liters (yep, more than the body actually contains). It comes down to the liver’s endless blood supply and sticky tissue that doesn’t hold stitches well.
- Open-Heart Surgery: Procedures like heart transplants or repairing a ruptured aorta can soak through dozens of units of blood because the heart pumps blood under serious pressure.
- Pelvic Trauma Surgery: Any surgery for smashing pelvic bones in an accident is a bloodbath waiting to happen. The area contains massive arteries and veins, which are tough to clamp or stitch during an emergency.
- Aortic Aneurysm Repairs: Fixing a ruptured aorta, the largest artery in the body, is a frantic race because blood loss can exceed two pints per minute.
- Complex Tumor Removal: Especially tumors entangled with major blood vessels. Surgeons cut, and the clean anatomical lines turn into a confusing mess.
Here’s a quick look at some real numbers:
| Surgery Type | Average Estimated Blood Loss | No. of Blood Units Transfused |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Transplant | 5-10 liters | Up to 30 units |
| Open-Heart Surgery | 2-6 liters | 5-20 units |
| Pelvic Trauma | 3-8 liters | 10-40 units |
| Aortic Aneurysm Repair | 2-6 liters | 5-15 units |
| Major Tumor Resection | 1-4 liters | Up to 10 units |
To put that into perspective, one unit of blood is only about 450 milliliters. In the worst cases, patients basically get a total blood "oil change" by the time the dust settles.
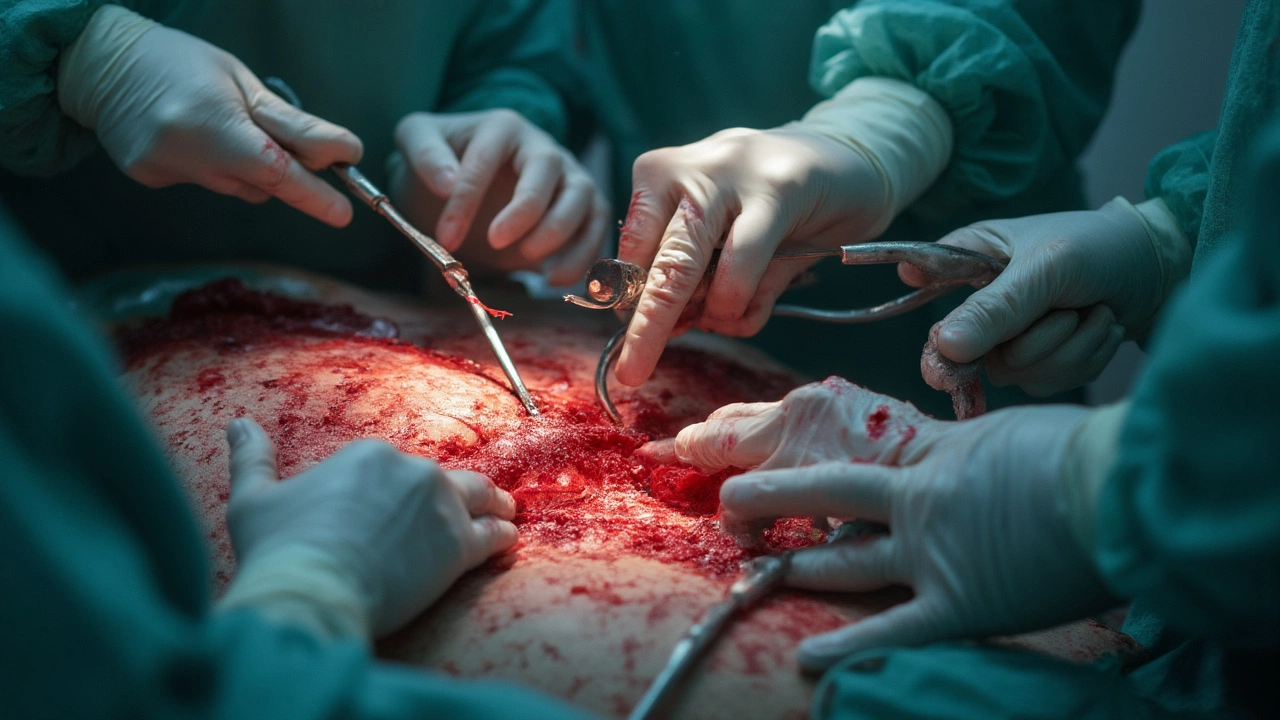
Inside the Operating Room: How Surgeons Tame the Bleeding
There’s a certain choreography at play during high-blood-loss operations. It’s fast, it’s noisy, and it’s anything but calm. Teams of surgeons, anesthesiologists, surgical techs, and nurses coordinate like a pit crew. Half the people are working on the patient, the other half rush blood and medications in at breakneck speed. Just a few years ago, a big liver transplant meant you’d see blood running down the drapes and pooling on the floor—yes, it really was that raw.
Now things have shifted a bit thanks to better training and clever tools. Here are tactics that keep the chaos under control:
- Massive Transfusion Protocol: This is a red alert for the blood bank to send tons of blood, platelets, and coagulation factors to the OR, STAT.
- Cauterization: Surgeons use heat to literally burn shut leaking blood vessels as they cut, minimizing spurting blood as much as possible.
- Topical Hemostatic Agents: Special sponges or sealants are packed onto tricky spots for clotting help.
- Temporary Clamps: Big arteries are pinched off with clamps while the team fixes the damage, then cautiously released at the end.
- Cell Savers: Sort of like vampire technology—these machines collect the patient’s spilled blood, filter it, and pump it back in real time.
Sometimes, it’s a game of speed, as in trauma surgery after a car wreck. Surgeons go for “damage control”: stop the bleeding, stabilize blood pressure, and then finish things later in a safer setting. It’s a wild ride where routines are thrown out the window, replaced by raw instinct and sometimes a heavy gut feeling. More than one study has shown that faster intervention—measured in minutes, not hours—can bump up survival odds by a whopping 30% or more.
What about the people managing the rest of the patient? Anesthesia teams often juggle drips and drugs to keep blood pressure up, temperature normal, and the heart beating strong even as blood loss ramps up. The record for the most units transfused in a single case? One mind-blowing story out of Texas in 2015: a trauma patient needed over 250 units—basically two entire human bodies’ worth of blood.
The Human Toll: Recovery After Extreme Blood Loss in Surgery
Leaving the operating room after one of these extreme cases is only half the battle. The body’s not meant to handle huge swings in blood volume, and neither is the mind. Patients who survive can face weeks in the ICU, dealing with complications like kidney failure, lung issues, and tricky infections.
It’s not as simple as swapping out “bad” blood for new. Every transfusion raises the odds of allergic reactions, clotting problems, or immune system changes. Recovery often means building red blood cells back up the old-fashioned way—slowly, with iron supplementation and rest. Some people battle months of weakness and exhaustion, and a few never quite feel the same again.
There’s also an emotional side most outsiders never see. Surviving a surgery that involved massive blood loss can trigger PTSD, depression, or nightmares. Surgeons and nurses occasionally need to process those intense cases just as much as their patients—after a marathon session, it’s common to see the whole team in a huddle, shoulders slumped, just soaking in the reality of what they pulled off. Families, too, often get shaken by the sight of their loved one attached to so many machines and tubes, pale and still, as if they’d been run through a warzone.
Tips for a smoother recovery after big blood-loss surgery?
- Plan for a longer hospital stay than you think. The body bounces back slowly.
- Get moving—but gently. Walking helps stave off blood clots and infections.
- Eat a protein-rich diet to support healing and red blood cell production.
- Stay connected with support groups if you feel anxious or overwhelmed.
- Ask questions early and often—no detail is too small when you’re regaining your strength.
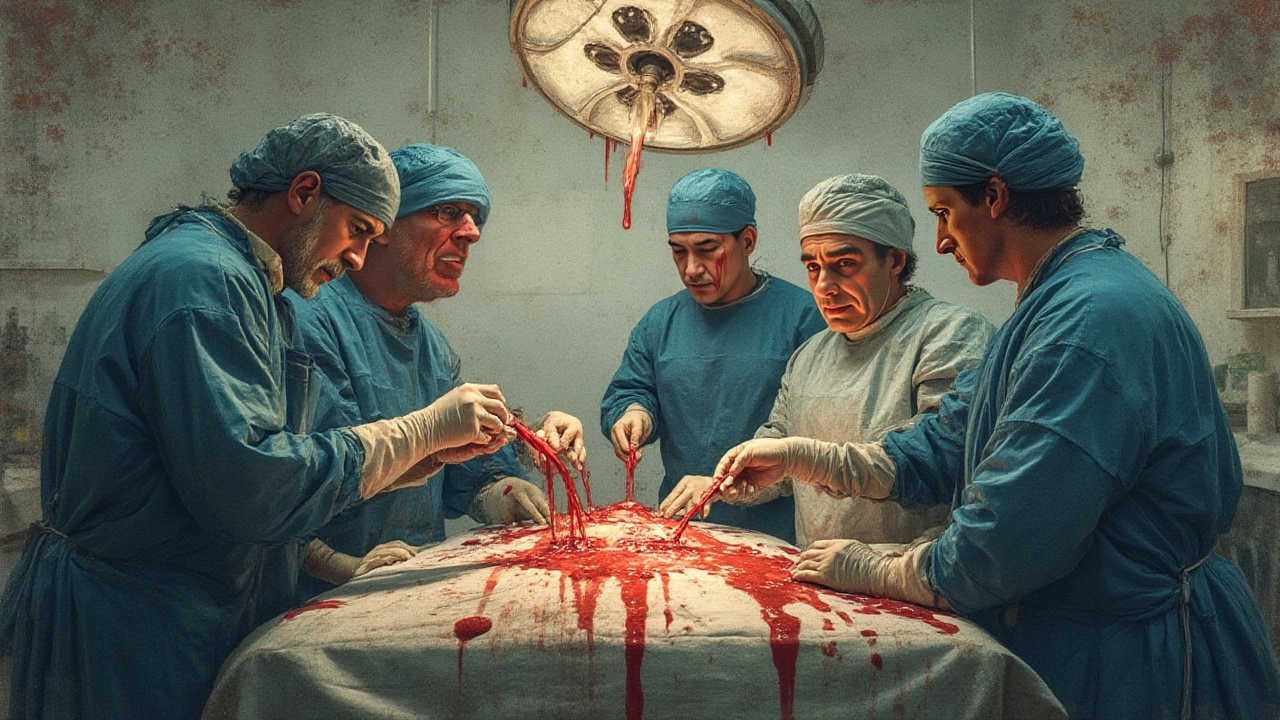
Reducing the Risk: How Doctors and Hospitals Prepare for High-Blood-Loss Surgeries
No one walks into a hospital hoping for a bloodbath, right? Hospitals plan every step carefully for high-risk surgeries, and tons of advances are making these procedures less terrifying than they used to be. Today, surgeons spend a lot of time beforehand checking a patient’s clotting ability, blood type, and underlying health—especially the heart and kidneys. If a patient’s blood “runs thin” (from medications like warfarin, or medical issues like hemophilia or cirrhosis), they’ll often get a tune-up first with meds or transfusions.
Modern protocols mean every “bloody” case on the schedule gets flagged on the hospital’s radar. Blood banks stockpile plenty of matching units. Some centers have blood on tap in the operating room, right there under a lock and key fridge. Simulation drills keep entire teams sharp, rehearsing massive transfusion events with dummies and fake blood to get everything down to muscle memory.
Even then, the unexpected can happen. That’s why surgeons always have a Plan B, C, and sometimes even D. Newer techniques are shifting away from open surgery to keyhole (laparoscopic) approaches, even for liver and heart operations, in hopes of less major artery slicing and dicing. Fibrin sealants, better cautery tools, and surgical glues are making a difference.
On the patient’s end, it pays to be honest about medical history and medications. Even a daily aspirin can change the bleeding game. If you know you’re walking into surgery with a risk for big blood loss, prepping with iron, eating well, and getting your hemoglobin checked ahead of time can make the road smoother. And if you’re ever in doubt, talk through the "plan for blood" with your surgical team—you’ll be amazed at how much better you’ll feel knowing there’s a game plan, not just hope and prayers.
